




Statutory compliance is a critical aspect of running a business, encompassing adherence to rules, regulations, and legal requirements set forth by governing authorities. Let's delve deeper into the importance of statutory compliance:
Statutory compliance is indispensable for businesses seeking sustainable growth, risk mitigation, and ethical conduct. By prioritizing compliance efforts, companies can uphold legal and ethical standards, safeguard their operations, and contribute to the overall well-being of society.
Legal Obligation: Compliance with statutory requirements is not just a choice but a legal obligation for businesses. Failing to comply with applicable laws and regulations can lead to severe legal consequences, including fines, penalties, and even legal action against the company.
Protection of Rights: Statutory compliance ensures the protection of the rights and interests of employees, customers, stakeholders, and the public at large. It encompasses various aspects such as minimum wages, working hours, safety standards, environmental regulations, and consumer protection laws.
Business Continuity: Adhering to statutory requirements is crucial for ensuring the continuity of business operations. Non-compliance can disrupt operations, damage the company's reputation, and even lead to closure in extreme cases. Compliance provides stability and fosters trust among stakeholders.
Enhanced Reputation: Compliance with statutory requirements enhances the company's reputation and credibility in the eyes of customers, investors, and the public. It demonstrates the company's commitment to ethical business practices, corporate responsibility, and regulatory compliance, thereby building trust and goodwill.
Avoidance of Penalties: Non-compliance with statutory requirements can result in hefty penalties, fines, and sanctions imposed by regulatory authorities. By adhering to regulations, businesses can avoid such penalties and preserve financial resources for investment and growth initiatives.
Employee Welfare: Compliance with labor laws and regulations ensures the welfare and rights of employees, including fair wages, safe working conditions, and protection against discrimination and harassment. It fosters a positive work environment and promotes employee loyalty and satisfaction.
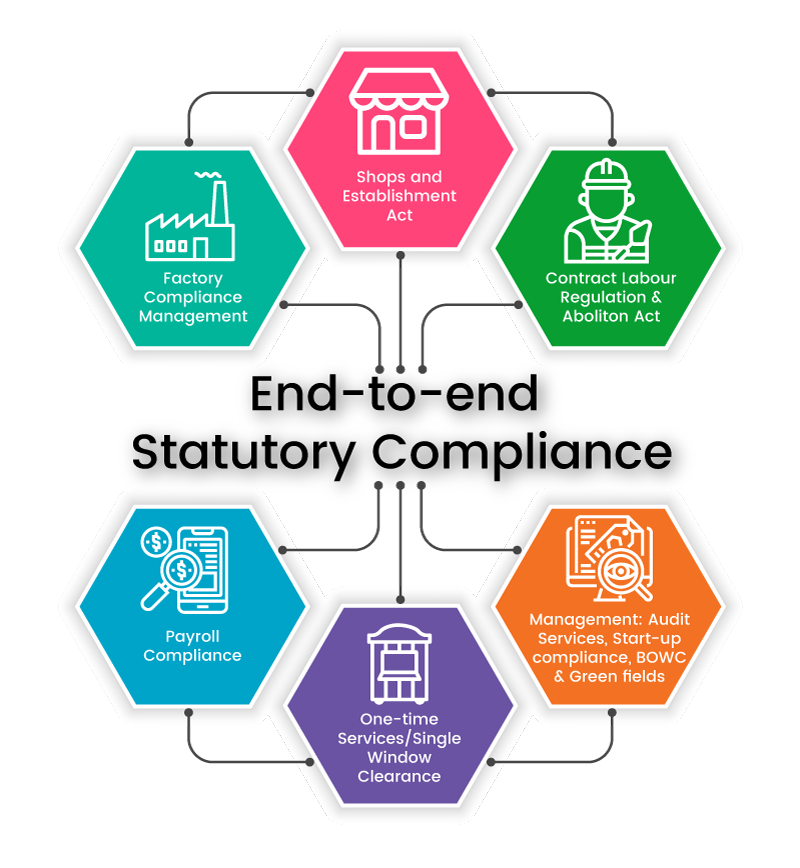
List of statutory compliance must follow by organization,
This act protects and safeguards employees working in shops and commercial establishments by providing guidelines for payment of wages, hours of work, leave, holidays, terms of service, and other work conditions.
The EPF Act was established to ensure the social security and welfare of employees by managing employer and employee contributions in the Employee Provident Fund Account.
The act was incorporated to provide social security and relief to employees in case of medical emergencies.
: This act specifies the amount and percentage at which tax is payable by a person earning an income from salary or anyone practicing a profession such as a chartered accountant, company secretary, lawyer, doctor, etc.
: The labour welfare fund act defines facilities and regulations to improve the working conditions and standard of living for labours.
: This act provides prohibition for an establishment to employ contract labour in any operation.
This act provides prohibition for an establishment to employ child labour in any operation.
This act defines the minimum rates of wages in certain employments.
This act regulates the timely and accurate payment of wages to employees and provides provisions for the deduction of certain amounts from wages.
This act ensures the payment of a bonus to employees based on their performance and the profits of the organization. It sets guidelines for calculating and distributing bonuses.
This act aims to provide maternity benefits to women employees, including maternity leave, medical benefits, and other related provisions.
This act mandates the payment of gratuity to employees who have served a certain period with an organization. Gratuity is a lump sum amount given as a retirement benefit.
This act promotes gender equality in the workplace by ensuring that men and women receive equal pay for equal work.
This act addresses the issue of sexual harassment at workplaces and mandates employers to establish mechanisms for preventing and addressing such incidents.
Formerly known as the Workmen's Compensation Act, this act provides compensation to employees for injuries or accidents that occur during the course of employment.
This act requires employers to define certain terms and conditions of employment through standing orders, providing clarity on various aspects of the employment relationship.
This act provides a framework for the resolution of industrial disputes, including procedures for negotiations, conciliation, and arbitration.
This act regulates apprenticeships, providing a legal framework for the
training and welfare of apprentices in various industries.
The
Interstate Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of
Services) Act, 1979: This act safeguards the interests of interstate migrant
workers by providing certain protections and regulating their employment
conditions.
This act sets out provisions related to the health, safety, and welfare of workers in factories. It covers various aspects of factory operation and worker protection.
This act governs the formation, registration, and functioning of trade unions, which are organizations representing workers' interests and rights


| MONTH & DATE WISE/TIME LIMIT | NAME OF RETURN OR COMPLAINCE |
UNDER THE ACT | FORM | TO WHOM/WHERE | |
| 15 | Remittance of Contributions | EPF & MP Act, 1952 | Challan to be generated ‘online’ | Pay ‘online’ or by submission of challan with cheque in the authorised banks | |
| 15 | Entitlement of every international worker with nationality and wages (I.W.) | EPF & MP Act, 1952 | Statement IW-1 Form 5 & 2 | Concerned Regional Office | |
| 21 | Remittance of Contributions | ESI Act, 1948 | Challan to be generated ‘online’ | ||
| MOTH DATE WISE/TIME LIMIT |
NAME OF RETURN OR COMPLAINCE |
UNDER THE ACT | IN WHICH FORM | TO WHOM/WHERE | |
| 15 days prior | Requisition of vacancies | Employment Exchanges (CNV) Act,1959 & Rules | Requisition Form, Rule 4 | Local Employment Exchange | |
| within 15 Days | Return/Notice within 15 days of commencement or completion of each contract by the Principal employer | Contract Labour (R&A) Act, 1970 | Form VI-B, Rule 81(3) | Concerned Inspector under the Act | |
| Notice of commencement/completion of contract work by the Contractor within 15 days | Contract Labour (R&A) Act, 1970 | Form VI-A, Rule 25(2)(VIII) | Concerned Inspector under the Act | ||
| Annual Return in duplicate. Not later than 15 Feb following the end of each calendar year | Building and Other Construction Workers (RE&COS) Act & the Rules,1966 | Form XXV | Registering Authority having jurisdiction | ||
| Within 30 Days from due dates | Quarterly Return for quarter ended 31st March | Employment Exchanges (CNV) Act,1959 & Rules | Form ER-1: Rule 6 | Local Employment Exchange | |
| Quarterly Return for quarter ended 30th June | Employment Exchanges (CNV) Act,1959 & Rules | Form ER-1: Rule 6 | Local Employment Exchange | ||
| Quarterly Return for quarter ended 30th September | Employment Exchanges (CNV) Act,1959 & Rules | Form ER-1: Rule 6 | Local Employment Exchange | ||
| Quarterly Return for quarter ended 31st December | Employment Exchanges (CNV) Act,1959 & Rules | Form ER-1: Rule 6 | Local Employment Exchange | ||
| Notice of applicability of the Act & any change | Payment of Gratuity Rules | Form A or B, Rule 3(1&2) | Controlling Authority | ||
| Application for renewal of licence in triplicate not less than 30 days before expiry of licence by contractor | The Contract Labour (R&A) Act, 1970 | Form VII: Rule 29(2) Refer to State Rules | Concerned Licencing Officer | ||
| Notice of commencement and completion atleast 30 days before commencement | Building and Other Construction Workers (RE&COS) Act & the Rules,1966 | Form IV | Concerned Inspector | ||
| Return about levy of collection of Cess | Building and Other Construction Workers (RE&COS) Act & the Rules,1966 | Form I, Rule 6 | Concerned Authority | ||
| Intimation about commencement of work within 30 days of the commencement of work | Building and Other Construction Workers (RE&COS) Act & the Rules,1966 | Form IV, Rule 26(3) & 239(1) | Assessing Officer | ||
| Biennial return within 30 days of the due date as notified in the official gazette | Employment Exchange (CNV) Act, 1959 & Rules | ER-II | Local Employment Exchange | ||
| MONTHH | DATE | WHICH COMPLIANCE | UNDER THE ACT | IN WHICH FORM | TO WHOM/WHERE |
| JAN | 15 | Annual Returns | Factories Act ,1948 | Form as prescribed in State Rules | Chief Inspector/Director or other competent authority of the area |
| JAN | 21 | Annual returns & details of payment ending 31st Dec | Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 | Forms L, M, N, & O: Rule16(1) | Competent Authority under the Act |
| JAN | 30 | Half yearly return by contractor (in duplicate) | Contract Labour ( R & A) Act, 1970 & Rules | Form XXIV: Rule 82(1) | Concerned Licencing Officer |
| JAN | 31 | Annual information about factory/ establishment covered | Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948 | Form 01A: Regulation 10C | Regional office (RO) or Sub.RO or Divisional Office |
| FEB | 1 | Annual Return | Minimum Wages Act, 1948 | Form III :Rules 21 (4A) | Concerned Inspector |
| FEB | 15 | Annual return by Principal Employer | Contract Labour ( R & A) Act, 1970 & Rules | Form XXV Rule 82(2) | Concerned Registering Officer |
| FEB | 15 | Annual return by Principal Employer | The Building and Other Construction Workers (RE&COS) | Form XXV Rule 242 | Regional Labour Commissioner |
| JUL | 15 | Half-yearly Return | Factories Act, 1948 | Form as prescribed in State Rules | Concerned Director/Inspector |
| JUL | 30 | Half-yearly Return, by Contractor (in duplicate) | Contract Labour ( R & A) Act, 1970 & Rules | Form XXIV: Rule 82(1) | Concerned Licencing Officer |
| DEC | 30 | Annual Return, within 30 days after the expiry of 8 months from the close of the accounting year | Payment of Bonus Act, 1965 & Rules | Form D: Rule 5 | Concerned Inspector under the Act |
| DEC | 30 | Annual Return, in such form and at such time as may be prescribed | Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace(PD&R) Act, 2013 | As may be prescribed | Employer/District Officer (yet to be notified) |
| IN CASE OF | NAME OF RETURN OR COMPLAINCE |
UNDER THE ACT | FORM ETC |
TO BE SENT TO | |
| Accident | Report immediately if fatal/death & within 48 hrs in ordinary cases | ESI Act, 1948 | Form 12 or online also | Concerned Local Office/Dispensary of ESI |
|
| Accident/dangerous occurrence | Notice Forthwith of occurrence | The Factories Act ,1948 | as prescribed in State Rules | Inspector/Director of Factories |
|
| Accident | Report within 12 hours of occurrence | The Factories Act ,1948 | as prescribed in State Rules | Director/Inspector of Factories |
|
| Serious bodily injuries/fatal accidents | Report within 7 days of accident | The Employees’ Compensation Act, 1923 | Form EE | Concerned Commissioner of Employees’ Compensation |
|
| Accident | Notice of accident within 4 hours in case of fatal accident and 72 hours in case of other | The Building and Other Construction Workers (RE&COS) Act & the Rules, 1966 | Form XIV, Rule 210 (7) | Regional Labour Commissioner |
|
© 2024 IKAMATE 2024 Ikamate HR India Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved. | Design By Dng Web Developer